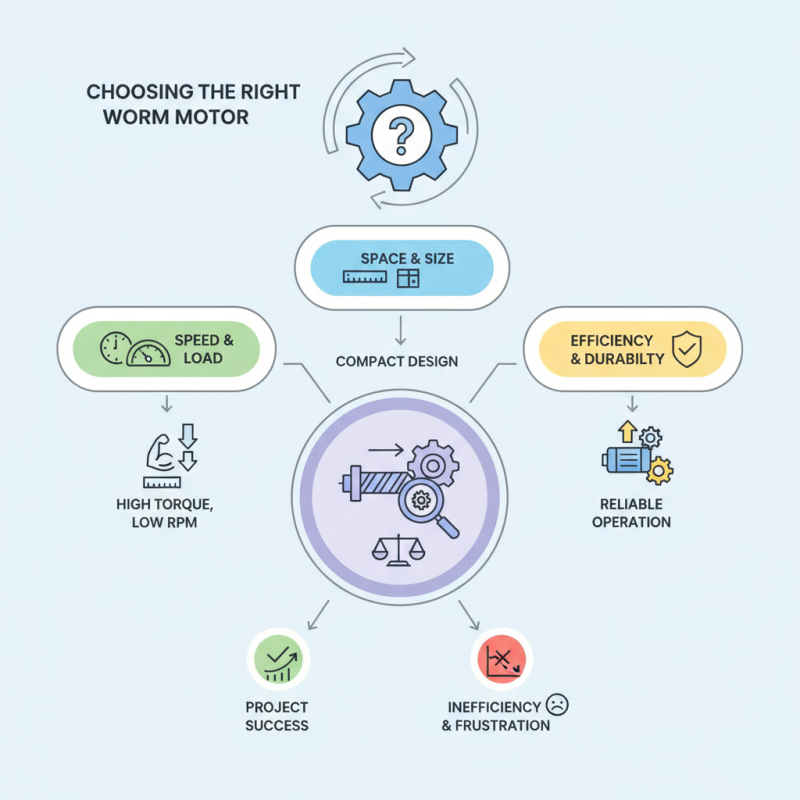
Choosing the right Worm Motor for your project can be challenging. There are many factors to consider. A worm motor is designed to reduce speed while increasing torque. It might be the best choice for applications requiring high torque at lower speeds.
When selecting a worm motor, think about your specific needs. Consider the desired speed, load capacity, and available space. The motor's efficiency and durability are also essential. Not all worm motors are created equal. Some may not meet your project requirements. It's crucial to research various options.
Reflect on your project’s unique challenges. An incompatible worm motor can lead to inefficiencies. It may even compromise your project's success. Take your time to weigh your options carefully. The right decision now can save you time and frustration later.
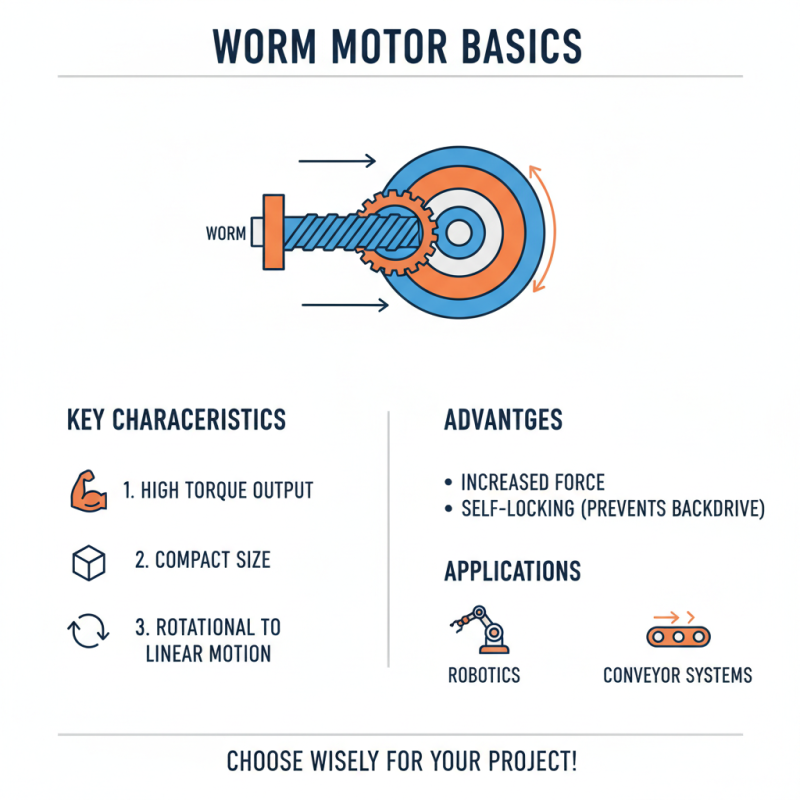
When selecting a worm motor for your project, it's crucial to grasp their fundamental characteristics. Worm motors are unique for their ability to provide high torque in a compact size. They convert rotational motion into linear movement with a gear ratio that increases the output force. This is advantageous in applications like robotics and conveyor systems.
One tip is to consider the load and speed requirements. Calculate the required torque needed for your application. Sometimes, projects demand more torque than expected. Underestimating this can lead to motor failure.
Another important aspect is the direction of rotation. Worm motors typically allow for unidirectional movement. This design can be a limitation if your project requires bi-directional motion. Think through these minor details as they can impact the overall project.
You might find yourself needing to recalibrate your expectations. Sometimes, experimenting with different gear ratios can yield unexpected results. In any case, understanding these basics helps ensure you select the right motor for your needs.

Selecting the right worm motor for your project requires careful consideration of several key factors. The motor's gear ratio plays a vital role. A higher gear ratio typically provides more torque but less speed. According to industry reports, a ratio of 10:1 is common for applications needing moderate torque and speed. Think about the project's specific needs when assessing gear ratios.
Another crucial aspect is the motor size and weight. Space constraints often dictate the size you can use. For instance, compact motors can save space but might sacrifice power. Studies have shown that smaller motors can still deliver up to 65% efficiency, depending on the application. Balance efficiency and power requirements.
Don't forget about thermal management. Worm motors can generate heat during operation. Excess heat can lead to inefficiencies or damage. It's essential to consider the operating environment. For example, operating in a high-temperature area might require additional cooling solutions. Reflecting on these factors is key to your success in selecting the right worm motor.
Selecting the appropriate worm motor for your project hinges on understanding torque and speed requirements. Torque is a vital factor, dictating the motor's ability to perform work. According to industry reports, many applications need around 0.5 to 5 Nm of torque for effective operation. However, certain projects might require much higher torque levels. For instance, robotic arms often demand torque figures in the tens of Nm. Assessing the load and mechanical advantages is crucial here.
Speed is equally important. Most worm motors offer a reduction ratio between 10:1 and 300:1. This means a motor could convert high RPM into useful low-speed power. A report highlighted that many automation systems operate optimally between 30 to 120 RPM. Consider your application’s pace demands. Slow-moving conveyors may thrive on lower speeds, while position-critical tasks may require fine control at varying speeds.
Project requirements can fluctuate, which may complicate your decision. If the torque and speed are miscalculated, your design may fail. For example, selecting a motor without sufficient torque may lead to stalled operations. Similarly, overestimating speed could result in mechanical failures. Ensuring precise calculations and adjustments in your design process is essential for success.
| Motor Type | Rated Torque (Nm) | Max Speed (RPM) | Input Voltage (V) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Worm Gear Motor A | 5.0 | 100 | 24 | Conveyor Systems |
| Worm Gear Motor B | 10.0 | 80 | 48 | Robotics |
| Worm Gear Motor C | 15.0 | 60 | 12 | Industrial Automation |
| Worm Gear Motor D | 20.0 | 40 | 230 | Heavy Machinery |
When selecting a worm motor, size and weight are critical factors. These parameters dictate how well the motor fits in your project. Oversized motors can be cumbersome, impacting design and functionality. Conversely, too small a motor may lack the necessary torque. Assess the space available in your project before making a choice.
Mounting options also play a significant role. A secure mount ensures stability during operation. Various configurations exist, from bracket mounts to panel mounts. Choose a method that works best with your design. However, some mounting solutions may complicate assembly. This aspect demands careful thought and planning.
Remember, each project is unique. Reflect on your specific needs before finalizing your motor selection. Weigh the pros and cons of your options. This requires patience and a willingness to reconsider previous choices. The right worm motor can enhance your project significantly, but one misstep could lead to failures down the road.
When selecting a worm motor, considering materials and construction types greatly influences performance. Common materials for worm motors include aluminum, steel, and plastic. Aluminum is lightweight and resistant to corrosion, which enhances durability. On the other hand, steel offers high strength and is better for heavy-duty applications. Plastic, while less durable, can provide cost-effective solutions for lighter loads.
The construction type also plays a key role in efficiency. Helical gears, for instance, deliver smoother operation compared to straight gears. According to the American Gear Manufacturers Association, the efficiency of helical gear designs can reach up to 95%. However, these designs often require precise alignment, increasing the complexity of assembly. Some manufacturers report that improper alignment leads to increased wear and reduced lifespan of the motor.
Additionally, it's essential to consider environmental conditions. For applications exposed to moisture or corrosive substances, using stainless steel or protective coatings is advisable. Research shows that motors operating in harsh environments tend to fail 30% sooner than those in optimal conditions. It's crucial to evaluate specific project needs to avoid costly redesigns and failures in performance.