In the rapidly evolving landscape of automation and electric drives, understanding the different types of DC motors and their specific applications is crucial for modern engineering solutions. According to a report by the International Electrotechnical Commission, the demand for DC motor technology is projected to grow significantly, driven by advancements in robotics and electric vehicles. Notably, industry expert Dr. Emily Carter remarked, "The versatility of DC motors, including the specialized 'Dc Dc Motor' variant, plays a pivotal role in enhancing operational efficiency across various sectors."
As industries increasingly adopt automation to boost productivity, the significance of selecting the right type of DC motor cannot be overstated. From precise control in robotics to reliable performance in consumer electronics, the diverse applications highlight the fundamental role these motors play in driving innovation. Recent studies indicate that the global market for DC motors is expected to exceed $10 billion by 2025, showcasing the importance of adapting motor technology to meet the dynamic needs of the industry. By examining the top 10 common types of DC motors, including the essential "Dc Dc Motor," we can gain insights into their functionalities and applications, paving the way for more efficient and effective engineering practices.

DC motors, or direct current motors, are electric machines that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy through the interaction of magnetic fields. These motors operate on the principles of electromagnetism, where a current-carrying conductor experiences a force in the presence of a magnetic field. This fundamental mechanism allows DC motors to provide variable speed and torque, making them highly versatile in a range of applications.
Tips: When selecting a DC motor for your project, consider the required speed and torque specifications. Understanding the load conditions will help you choose an appropriate motor type and size to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Most commonly, DC motors are classified into various types, including brushed, brushless, series, shunt, and compound motors, each serving distinct purposes. For instance, brushed DC motors are often utilized in simple applications due to their straightforward design, while brushless motors are preferred in applications requiring higher efficiency and precision, such as robotics and ventilation systems.
Tips: Always factor in the operating environment of the motor. Motors with specific protection ratings may be necessary for applications exposed to dust, moisture, or extreme temperatures, ensuring reliability and safety.
This bar chart represents the top 10 common types of DC motors and their applications in various industries. Each motor type is evaluated based on its application frequency, showcasing the versatility of DC motors across different sectors.
DC motors are widely used in various applications because of their simplicity and efficiency. They can be classified into several types based on their construction and operational characteristics. The main classifications include brushed DC motors, brushless DC motors, stepper motors, and servo motors. Brushed DC motors are known for their reliability and ease of control, making them a popular choice for everyday applications like toys and household appliances. In contrast, brushless DC motors provide higher efficiency and longer life by eliminating the need for brushes, making them ideal for computer peripherals and electric vehicles.
When considering the type of DC motor to use, it's essential to understand the key characteristics of each type. For instance, stepper motors excel in precision control and are often utilized in applications requiring accurate position control, such as 3D printers and robotic arms. On the other hand, servo motors are designed for applications where precise control of angular position, velocity, and acceleration is necessary, such as in industrial automation and aerospace systems.
Tips: When selecting a DC motor, evaluate the torque, speed, and power requirements of your application. Ensure that the motor's voltage and current ratings align with your system's parameters. Additionally, consider the environment where the motor will operate, as dust and moisture can impact performance and longevity.
DC motors are fundamental in various applications due to their precise control and efficiency. Among the most common types are brushed DC motors, often utilized in simple applications requiring low to moderate torque. They are widely employed in toys, automotive starters, and small appliances, offering ease of control and straightforward maintenance. In contrast, brushless DC motors, which are known for their longevity and lower maintenance needs, find their niche in high-performance applications such as electric vehicles and computer hard drives. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global brushless DC motor market is projected to reach $40 billion by 2025, demonstrating their increasing relevance in modern technology.
Another significant type is the stepping motor, which offers precise control of angular position. This unique capability is leveraged in devices like 3D printers and CNC machines, where accuracy is crucial. The North American market for stepping motors was valued at approximately $1.5 billion in 2020, highlighting their importance in industrial applications. Furthermore, servo motors, often used in robotics and automation, provide high torque and speed control, making them indispensable in manufacturing processes.
Tips: When selecting a DC motor for your application, consider factors such as load requirements, desired speed control, and the environment in which the motor will operate. Always refer to the latest industry reports to stay informed about emerging trends and technologies that can enhance your application’s efficiency.
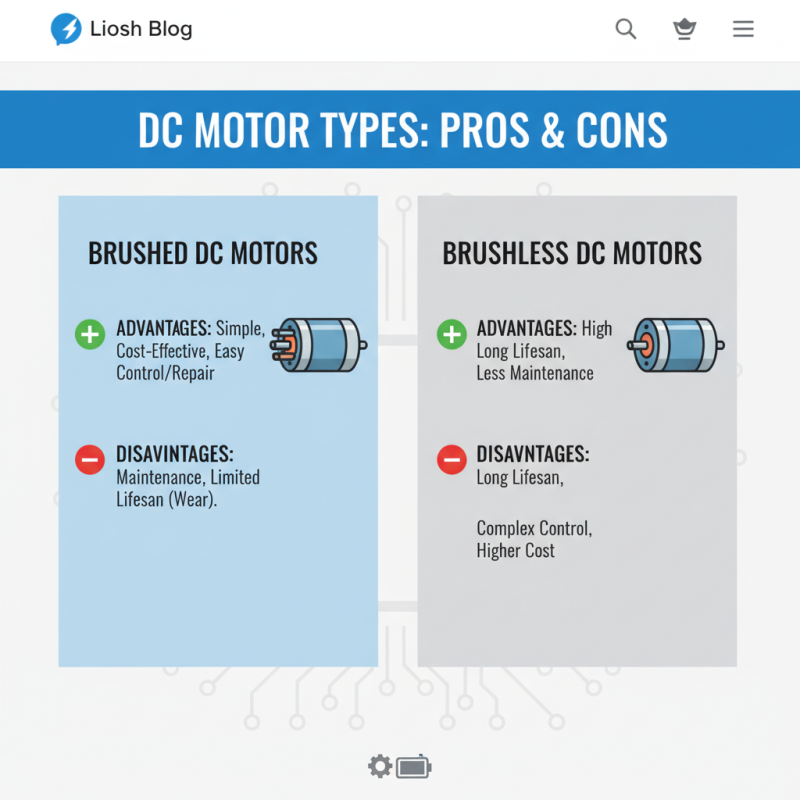
When evaluating different types of DC motors, it's essential to consider their advantages and disadvantages, as these factors can significantly impact their suitability for various applications. Brushed DC motors are straightforward and cost-effective, making them ideal for low-power applications. Their simplicity allows for easy control and repair; however, the presence of brushes means they require maintenance and have a limited lifespan due to wear and tear.
On the other hand, brushless DC motors, while typically more expensive, offer higher efficiency and durability. Without brushes, they generate less heat and operate quietly, making them preferable for high-performance applications like robotics and electric vehicles. However, their complexity and the need for advanced control systems can pose challenges for users. Additionally, other types, such as stepper motors, excel in precise positioning but may not handle continuous load scenarios well. Understanding these aspects is crucial for making informed decisions for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of the motor system.
When selecting a DC motor for specific use cases, it’s crucial to consider various factors including torque requirements, speed control, and application environment. Different types of DC motors, such as brushed and brushless motors, offer unique benefits that make them suitable for specific applications. For example, brushed DC motors are typically easier to control and are a cost-effective solution for small devices requiring simple motion control. In contrast, brushless DC motors provide higher efficiency and longer lifespans, making them ideal for more complex applications like robotics and electric vehicles.
Tips: Before making a decision, assess the operating conditions of your application. Consider factors such as load variations, space constraints, and environmental conditions, such as temperature and moisture levels. Understanding these factors will help ensure that the chosen motor can reliably perform in its intended environment.
Also, take into account the method of speed regulation. Applications requiring precise speed control may benefit from DC motors equipped with feedback systems, while simpler applications might operate effectively with a basic variable resistor or PWM control. This consideration will help you strike the right balance between performance and cost-effectiveness, enabling the successful implementation of your project.
| Motor Type | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Brushed DC Motor | A simple motor with brushes for commutation. | Robotics, toys, and automotive applications. |
| Brushless DC Motor | Uses electronic commutation, eliminating the need for brushes. | Computer fans, drones, and electric vehicles. |
| Coreless DC Motor | Lightweight motor with a coreless rotor for fast response. | Medical devices, precision instruments, and drones. |
| Permanent Magnet DC Motor | Uses permanent magnets for the magnetic field. | Electric bicycles, forklifts, and conveyors. |
| Step DC Motor | Moves in discrete steps for precise control. | 3D printers, CNC machines, and camera control systems. |
| Servo DC Motor | Designed for precise position control. | Robotics, radio-controlled vehicles, and automation systems. |
| Shunt-Wound DC Motor | Field winding is connected in parallel with the armature. | Lifts, fans, and general machinery. |
| Series-Wound DC Motor | Field winding is connected in series with the armature. | Electric vehicles, cranes, and winches. |
| Compound-Wound DC Motor | Combines shunt and series winding for better performance. | Industrial machinery, elevators, and fans. |