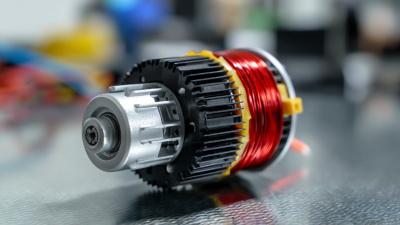
A DC motor in simple terms is an electromechanical device that converts direct current electrical energy into mechanical energy. This fundamental piece of technology plays a crucial role in various applications, ranging from small household appliances to large industrial machines. Understanding how a DC motor operates not only demystifies the technology behind it but also highlights its significant contributions to modern engineering and everyday life.
At its core, a DC motor functions through the interaction of magnetic fields and current flow. When an electric current passes through the motor's windings, it generates a magnetic field that interacts with the permanent magnets or electromagnets, causing the rotor to turn. This principle of electromagnetism is what allows DC motors to provide efficient and adjustable control over speed and torque, making them ideal for numerous applications.
In this exploration, we will delve deeper into the components of a DC motor, how it works, and its various types and uses. By gaining a better understanding of this vital device, we can appreciate the intricate mechanics that drive everything from toy cars to sophisticated robotics in today's technology-driven world.
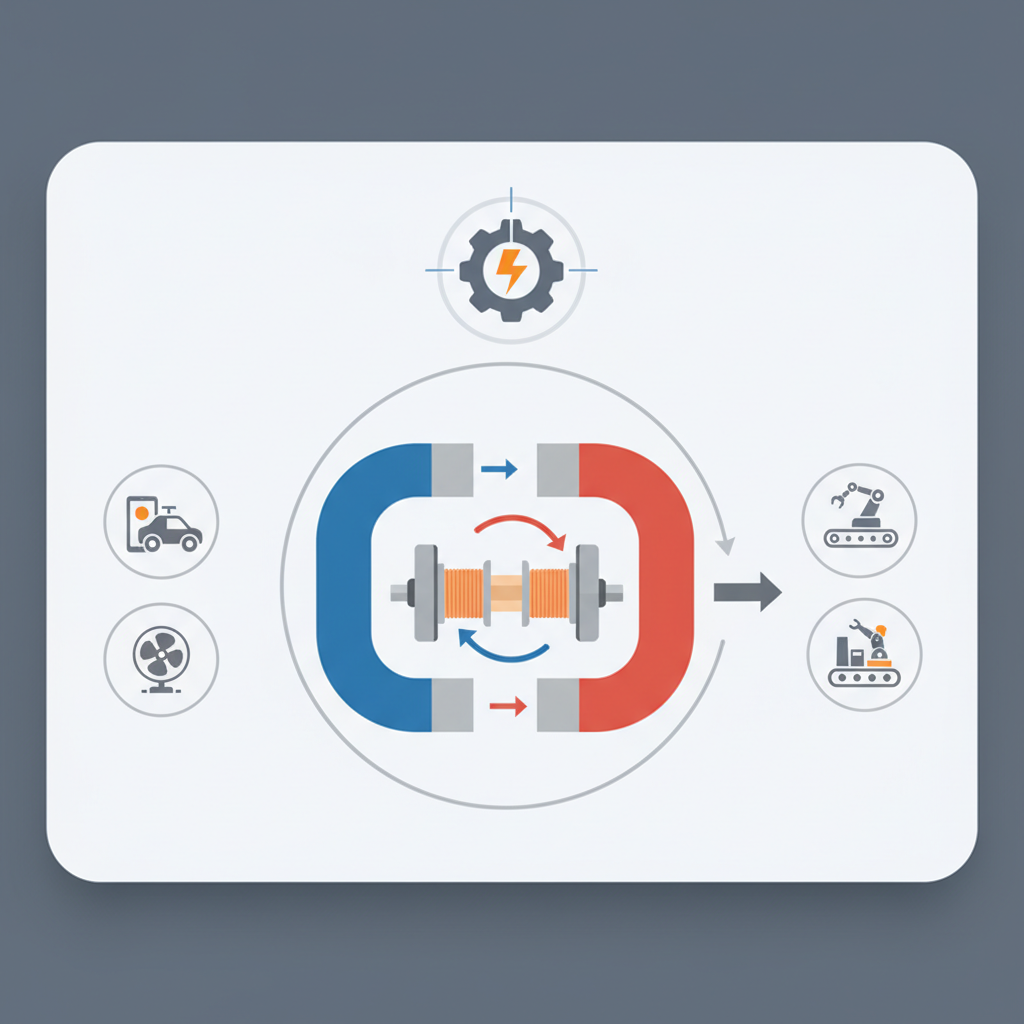
A DC motor is a type of electric motor that converts direct current electrical energy into mechanical energy. It operates on the principle of electromagnetism, where the interaction between a magnetic field and a current-carrying conductor results in motion. In simple terms, when electricity flows through the motor's windings, it creates a magnetic field that interacts with permanent magnets or another set of windings, causing the rotor to spin. This spinning motion is what ultimately drives the wheels of electric vehicles (EVs).
In the context of the growing electric vehicle market, understanding the role of DC motors is crucial. According to industry reports, DC motors are favored in many EV applications due to their simplicity, reliability, and ease of control. For instance, a report from a leading automotive research firm indicates that DC motors account for approximately 55% of the total motor market in electric vehicles, owing to their efficient torque production and relatively low manufacturing costs. Additionally, with advancements in technology, the efficiency of DC motors has improved, enabling vehicles to achieve better performance metrics, including increased acceleration and energy efficiency, which enhances overall driving range and user experience.
A DC motor is a type of electric motor that converts direct current electrical energy into mechanical energy. Understanding its basic components is crucial for grasping how it operates. The primary elements of a DC motor include the stator, rotor, brushes, and commutator.
The stator is the stationary part of the motor and typically consists of permanent magnets or electromagnetic windings. It establishes the magnetic field necessary for motor function. The rotor, or armature, is the rotating component that interacts with the magnetic field, enabling movement. Brushes made of conductive material, like carbon, facilitate electrical contact with the rotor. Finally, the commutator serves to reverse the direction of current flow through the rotor windings, ensuring continuous rotation.
Tips: When working on DIY projects involving DC motors, ensure proper alignment of the brushes for optimal performance. Additionally, always check the voltage ratings to avoid damaging the motor. Understanding the interplay between these components will significantly improve your ability to troubleshoot and optimize motor efficiency.
A DC motor operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, which converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. At its core, the motor consists of a rotor and a stator.
The rotor, or armature, is the rotating component that generates motion, while the stator provides a magnetic field. When direct current flows through the armature winding, it creates a magnetic field that interacts with the fixed magnetic field of the stator. This interaction produces a torque that causes the rotor to turn.
The direction and speed of the rotor can be controlled by varying the voltage supplied to the motor. Increasing the voltage results in a stronger magnetic field, leading to faster rotation. Additionally, the direction of the current can be reversed to change the rotation direction of the motor. This simple yet effective mechanism enables DC motors to be used in various applications, such as electric vehicles, home appliances, and robotics, where precise control of movement is essential.
DC motors have gained significant popularity across various applications, especially in industrial automation and robotics. These motors can be categorized into several types, including brushed and brushless DC motors. Brushed DC motors are commonly used in inexpensive household appliances and toys due to their simplicity and robustness. On the other hand, brushless DC motors are preferred in applications requiring higher efficiency and longer operational life, such as in advanced robotic systems and electric vehicles.
In the automotive sector, the use of DC motors is expanding rapidly. Predictions show that the demand for electric motors in automotive window systems is expected to rise significantly between 2025 and 2033. This growth is partially attributed to the increased focus on automation and user comfort in vehicles. Moreover, as smart vehicle technologies develop, intelligent motor controllers are becoming essential for managing DC motors, facilitating improved vehicle performance and energy efficiency.
Tips for selecting a DC motor for your application include considering the specific torque requirements, sizing the motor correctly to prevent overheating, and evaluating whether a brushed or brushless type is more suited to your needs. Additionally, assessing the control method—open-loop versus closed-loop control—can significantly impact the motor's performance and suitability for a given task.

DC motors, known for their simplicity and efficiency, have distinct advantages and disadvantages that make them suitable for various applications. One of the primary advantages is their ability to provide high torque at low speeds, which is essential in applications requiring precise control, like robotics and electric vehicles. Additionally, DC motors are relatively easy to control with variable speed options, making them versatile in different operational environments.
On the downside, DC motors typically have a shorter lifespan due to brush wear in brushed motors. This wear can lead to increased maintenance requirements compared to brushless designs. Another drawback is their susceptibility to voltage and load variations, impacting performance stability.
Despite these challenges, advancements in motor technology, such as the shift from hydraulic systems to electric drive, are significantly improving motor performance in industries. For instance, the development of advanced electric motors is driving enhancements in electric vehicle performance, where factors like weight, efficiency, and compactness are crucial. Reports indicate that innovations in motor design have resulted in efficiencies exceeding 90%, further solidifying the role of DC motors in modern applications.