In the realm of engineering and technology, understanding the various motor kinds is essential for both professionals and enthusiasts alike. Motors serve as the backbone of countless applications, from small household appliances to large industrial machines. Each type of motor has unique characteristics that make it suitable for specific tasks, whether it be the high-torque demands of electric motors in heavy machinery or the low-power requirements of DC motors in portable devices.
This exploration of different motor kinds will shed light on their fundamental operating principles, design variations, and practical applications across diverse fields. By dissecting the most common types of motors, such as AC motors, DC motors, stepper motors, and servo motors, we can better appreciate how these machines convert electrical energy into mechanical energy, ultimately driving innovation and efficiency in modern technology. Whether in robotics, automotive, or manufacturing sectors, understanding motor kinds allows us to optimize their uses and harness their capabilities in an increasingly automated world.

Electric motors are essential components in various applications, and they can be categorized into several distinct types based on their design and the nature of their operation. The most common types are AC motors, which include both induction motors and synchronous motors, and DC motors, which are further divided into brushed and brushless variants.
AC induction motors are widely used due to their durability and simplicity, making them suitable for general applications such as fans, pumps, and compressors. Synchronous motors, on the other hand, are often employed in precision applications where speed consistency is crucial, such as in robotics and industrial machinery. In the realm of DC motors,
brushed motors are favored for small-scale applications like toys and handheld devices, while brushless motors are increasingly used in technologies requiring high efficiency and reliability, such as electric vehicles and HVAC systems.
These various motor types serve distinct purposes across industries, highlighting the versatility and importance of electric motors in modern technology.
DC motors play a pivotal role in both automotive and industrial applications due to their simplicity, efficiency, and high torque characteristics at lower speeds. In the automotive sector, DC motors are commonly used for essential functions such as power windows, seat adjustments, and windshield wipers. According to industry reports, the global automotive motor market is expected to reach $7 billion by 2025, driven by the increasing demand for electric vehicles, where DC motors are particularly favored for their ability to provide high starting torque and smooth variable speed control.
In industrial settings, DC motors are often employed in conveyor systems, robotics, and industrial machinery. Their precision and reliability make them ideal for applications requiring consistent performance. A study by MarketsandMarkets projects that the industrial automation market will grow to $296 billion by 2026, highlighting the increasing integration of DC motors within automated systems to enhance productivity and efficiency.
Tips: When selecting a DC motor for a specific application, always consider factors like load requirements, operational environment, and energy consumption. Additionally, proper integration and maintenance of these motors can significantly impact their lifespan and operational efficiency, thus maximizing their performance in both automotive and industrial contexts.
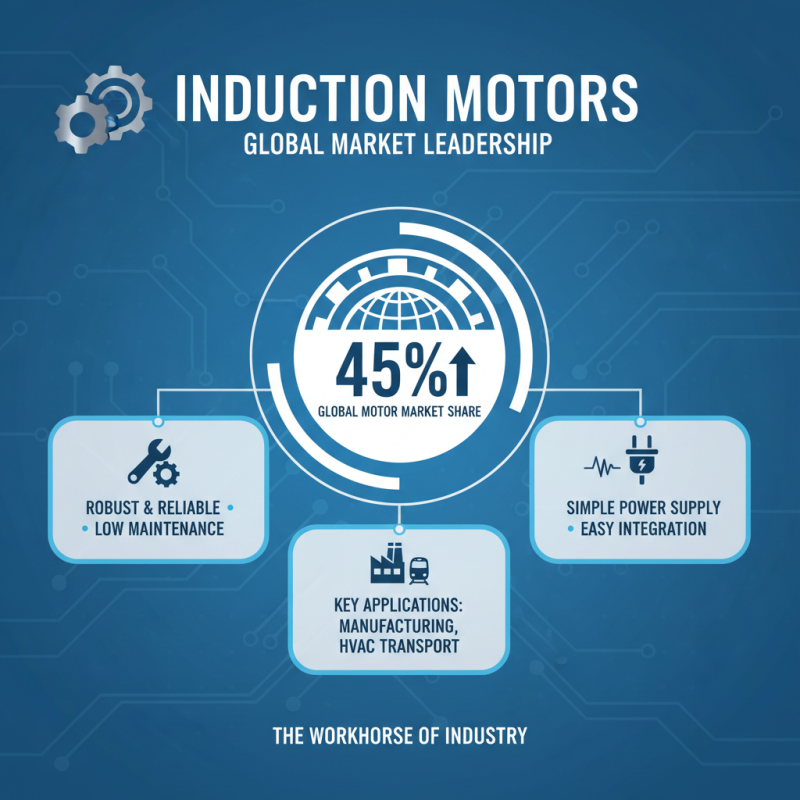
Induction motors are widely recognized for their robust performance and efficiency in various applications, making them a significant component of the electric motor market. According to recent industry reports, induction motors account for approximately 45% of the global motor market share, a figure driven by their increasing adoption in sectors such as manufacturing, HVAC systems, and transportation. These motors are favored for their reliability and low maintenance costs, which are crucial in environments where uptime is essential. The ability of induction motors to operate on a simple power supply, without the need for complex configurations, further enhances their appeal in industrial applications.
The key features of induction motors include their torque-speed characteristics and efficiency ratings. They usually exhibit high starting torque and can maintain good performance even under variable load conditions. Statistics indicate that the efficiency of modern induction motors has improved significantly, with many models achieving efficiencies of over 90%. This efficiency not only results in reduced energy consumption but also contributes to lower operational costs for businesses. Moreover, the growing emphasis on energy-efficient technologies is expected to drive further advancements in induction motor designs, aligning with global sustainability goals and regulations. As industries gear up for a more eco-friendly future, the role of induction motors will continue to evolve, solidifying their position in the market.
Stepper motors have emerged as a pivotal technology in various applications, particularly in robotics and 3D printing, where precision control is paramount. These motors operate by moving in discrete steps, allowing them to maintain high accuracy in positioning and speed. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global stepper motor market is projected to reach USD 4.3 billion by 2025, reflecting a substantial growth trend attributed to the rising demand for automation in industries.
In robotics, stepper motors are key components for actuating movement with reliability and precision. They are extensively used in robotic arms, where precise angle positioning is required. The ability to control the step size means that engineers can easily calibrate movements to the micro-level, enhancing the performance of robotic systems. Furthermore, in the field of 3D printing, these motors facilitate the fine layer-by-layer creation of objects, ensuring that the end product meets the desired specifications. Reports indicate that stepper motors contribute to an increased resolution in 3D printers, improving print quality and reducing material waste, which is critical in today's eco-conscious manufacturing landscape.
The versatility and reliability of stepper motors make them invaluable in advancing technologies that require stringent control over movement. As industries continue to push the boundaries of automation, the importance of stepper motors is expected to grow, driving innovation and efficiency across numerous fields.
| Motor Type | Description | Common Uses | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stepper Motor | A motor that divides a full rotation into a large number of steps for precise control. | 3D printing, CNC machines, robotics, and automation equipment. | High precision, excellent repeatability, and straightforward control. | Limited speed, torque drop-off at high speeds, and potential for resonance. |
| DC Motor | A motor powered by direct current that can provide high torque at low speeds. | Fans, toys, electric vehicles, and consumer appliances. | Simple design, easy speed control, and high starting torque. | Maintenance required due to brushes and commutators, less efficient than other types. |
| AC Motor | A motor that runs on alternating current and is widely used in industrial applications. | Pumps, fans, compressors, and industrial machinery. | Durable, low maintenance, and high efficiency for continuous operation. | Less precise speed control than DC and may require complex control systems. |
| Servo Motor | A motor designed for precise control of angular position, commonly used with a feedback system. | Robotics, conveyor systems, and CNC machinery. | High precision and quick response to changes in position. | Complex control circuits and more expensive than typical motors. |
Servo motors play a crucial role in the automation and aerospace industries due to their precision and reliability. In automation, servo motors are employed in applications such as robotics, conveyor systems, and CNC machinery. Their ability to provide accurate position control and rapid response to varying load conditions makes them essential for tasks that require high levels of precision. For instance, in robotic arms used in manufacturing, servo motors enable the exact movements needed for assembly, welding, and painting, ensuring efficiency and consistency in production processes.
In the aerospace sector, servo motors are utilized in flight control systems, where they adjust the position of control surfaces to maintain stability and maneuverability during flight. The critical nature of aerospace applications demands components that can operate under extreme conditions while maintaining high performance. Servo motors fulfill these requirements by offering robust construction and the capability to perform under strict safety standards. Their integration into systems like autopilots and landing gear further exemplifies their importance, ensuring that aircraft operate safely and smoothly. Thus, servo motors are indispensable to both industries, driving innovation and efficiency.
This bar chart illustrates the different types of motors commonly used in various industries, highlighting their respective applications. Servo motors play a critical role particularly in automation and aerospace sectors, represented by a significant share in the chart.