In today's fast-paced industrial environment, the need for efficient automation solutions has never been greater. Central to achieving this efficiency is the Gear Motor, a critical component that combines power transmission and motion control. Gear Motors play an indispensable role in various sectors, including manufacturing, logistics, and food processing, providing the necessary torque and precision for a multitude of applications. As industries strive to optimize their operations, the integration of Gear Motors enables the reliable and consistent functionality needed to enhance productivity and reduce downtime.
The significance of Gear Motors extends beyond mere mechanical operation; they symbolize the advancement of technology in industrial automation. By allowing for variable speed control and increased energy efficiency, these motors facilitate improved performance and operational sustainability. Furthermore, as businesses continue to adapt to evolving market demands, Gear Motors offer the flexibility required to implement innovative automation strategies. Therefore, understanding their essential role in automation is crucial for industries aiming to stay competitive and responsive to new challenges.
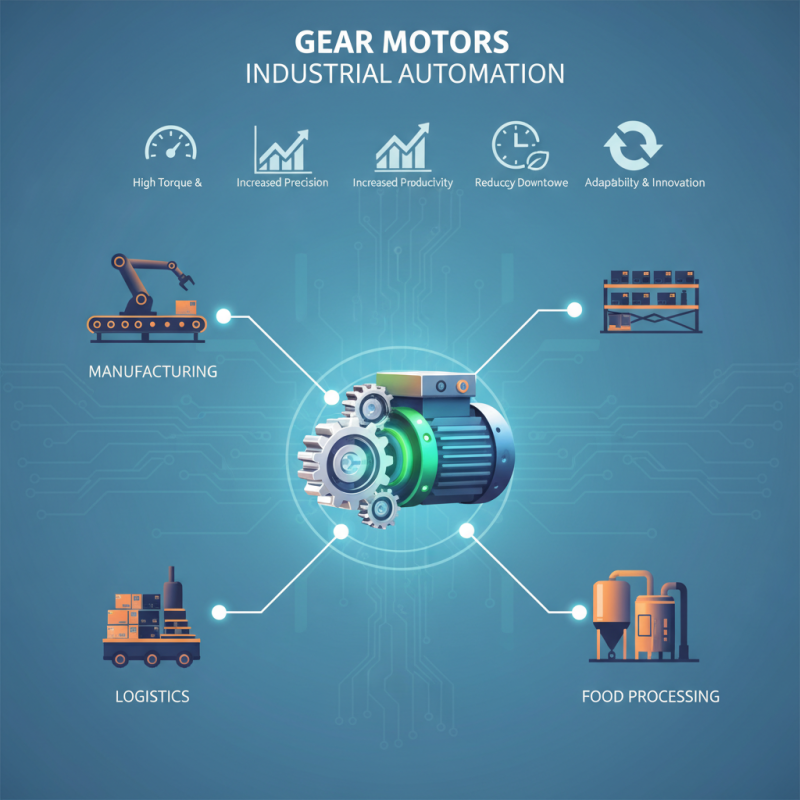
Gear motors play a pivotal role in optimizing automation processes across various industries. By converting energy from an electric source into mechanical power, they provide the necessary torque and speed control that are essential for efficient operation. This precision allows for better performance in tasks ranging from assembly lines in manufacturing to robotic movements in warehouses. The integration of gear motors not only enhances the speed of operations but also significantly improves the reliability and consistency of automated systems.
In addition to boosting operational efficiency, gear motors contribute to energy savings, a growing concern in today's industrial landscape. Their design often promotes lower energy consumption while still delivering high performance, which is crucial for companies looking to reduce their carbon footprint and operational costs simultaneously. Moreover, gear motors are versatile, accommodating various load requirements and environmental conditions, making them an invaluable asset for enhancing automation efficiency in industries such as automotive, food processing, and material handling. This adaptability further solidifies their status as an essential component in the pursuit of smarter, more efficient production solutions.
This chart illustrates the percentage increase in automation efficiency across various industries when using gear motors. The data showcases how gear motors contribute to enhancing production processes and reducing operational downtimes.
Gear motors play a crucial role in various industries, enhancing efficiency and reliability in automation processes. The manufacturing sector is a prime example, where gear motors are essential for driving conveyor systems, robotic arms, and other machinery. Their ability to provide precise control over speed and torque makes them invaluable for applications that require consistent performance, such as assembly lines and material handling systems.
Another key industry benefiting from gear motors is the automotive sector. Here, these motors are utilized in assembly robots and automated testing equipment, contributing to streamlined production processes. Additionally, the food and beverage industry relies on gear motors for mixing, packaging, and bottling processes, ensuring that operations run smoothly and safely in a fast-paced environment.
Tips: When selecting gear motors for your automation needs, consider the specific requirements of your application, such as load capacity and speed. It's also beneficial to assess the installation environment, as factors like temperature and humidity can impact motor performance. Regular maintenance is essential to prolong the lifespan of gear motors, so establish a routine check to ensure optimal function.
When considering drive technologies for automation, gear motors stand out due to their unique advantages over other systems, such as direct drives or servo motors. Gear motors, which combine a motor with a gearbox, significantly enhance torque output while reducing speed. This characteristic makes them particularly suitable for heavy-duty applications needing precise control and reliability. In contrast, direct drives may offer simpler designs and less maintenance, but they often lack the high torque capabilities required in many industrial settings. Servo motors, while excellent for applications requiring rapid motion, can be more complex and expensive, making gear motors a more cost-effective solution for numerous tasks.
Tips for selecting the appropriate drive technology include evaluating the specific torque and speed requirements of your application. Gear motors excel in scenarios demanding consistent torque under load, while other technologies may be better suited for variable speed applications. Additionally, consider the environmental conditions your equipment will face—gear motors are typically more robust and capable of withstanding harsh conditions compared to their counterparts. It's also essential to assess the total cost of ownership for each technology, as lower initial costs may not always translate to long-term savings.
Ultimately, gear motors provide a compelling combination of efficiency and performance, making them an indispensable choice for industries ranging from manufacturing to robotics. Selecting the right drive technology involves understanding the nuances of your operational needs and how each option aligns with your goals.
Gear motors play a pivotal role in enhancing automation efficiency across diverse industries. According to a recent report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), electric motors, which include gear motors, are responsible for about 45% of global electricity consumption in industrial applications. The integration of high-efficiency gear motors can reduce energy consumption by approximately 20-30%, providing significant cost savings and increasing operational sustainability.
Moreover, a 2022 study conducted by the American Gear Manufacturers Association (AGMA) revealed that industries employing gear motors to optimize their automation processes reported a 15% increase in productivity. This statistic underscores the crucial role that gear motors have in streamlining machinery, enabling smoother operations, and minimizing downtime. With automation becoming increasingly vital in manufacturing, logistics, and other sectors, the efficiency of gear motors not only contributes to lower energy bills but also enhances overall system performance, driving significant advancements in productivity and profitability.
| Industry | Efficiency Improvement (%) | Energy Savings (kWh/year) | CO2 Reduction (tons/year) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | 15% | 50,000 | 25 |
| Food Processing | 20% | 30,000 | 15 |
| Automotive | 12% | 40,000 | 20 |
| Textiles | 18% | 25,000 | 12.5 |
| Pharmaceuticals | 10% | 35,000 | 17.5 |

As industries continue to evolve, so too do the technologies that drive their operations. Innovative developments in gear motor technology are at the forefront of this transformation, enhancing efficiency and productivity across various sectors. Future trends indicate that advancements in materials science will lead to lighter and more durable gear motors, enabling high performance in demanding environments. Additionally, the integration of smart technologies and IoT capabilities into gear motors is set to revolutionize how industries monitor and manage their equipment, providing real-time data that aids in predictive maintenance and optimized performance.
Furthermore, energy efficiency remains a critical focus, with new gear motor designs emphasizing reduced power consumption while maintaining high output. These innovations not only contribute to operational cost savings but also align with the growing demand for sustainability in industrial practices. As automation becomes increasingly vital, the evolution of gear motors will play a crucial role in meeting the challenges of modern production processes, helping industries to achieve greater precision and reliability in their systems.