Power motors play a crucial role in today's technology. They convert electrical energy into mechanical motion. This conversion allows machines and devices to function efficiently across various applications. For instance, in industrial settings, power motors drive conveyor belts and pumps. They enhance productivity and operational speed.
In the automotive industry, power motors are vital for electric vehicles. They ensure smooth acceleration and energy efficiency. Despite their advantages, the complexity of power motors can pose challenges. Maintenance and troubleshooting require specialized knowledge. Understanding these motors can lead to better performance and longevity.
Reflecting on the importance of power motors, we must consider their environmental impact. As we strive for sustainability, innovations in power motor technology are essential. Improved designs can reduce energy consumption and increase efficiency. However, continuous improvement is necessary to meet future demands. Power motors are not just about functionality; they also hold potential for advancement.

A power motor is a mechanical device that converts electrical energy into rotational motion. Unlike regular motors, power motors usually operate at higher voltages and currents. These motors are crucial in various industries, enabling machinery and equipment to function efficiently. They come in different types, such as AC and DC motors, each with its unique applications.
In industrial settings, power motors are often used in conveyor belts, pumps, and compressors. For example, a power motor can drive the belt of a conveyor system that transports materials. The efficiency of these motors significantly affects productivity. However, improper selection or installation can lead to performance issues. For instance, overloading a motor may cause it to overheat and fail.
In automotive applications, power motors function in electric vehicles and hybrid systems. They provide torque to the wheels, leading to smoother acceleration. Nevertheless, not all power motors are compatible with every vehicle design. Designers must carefully consider the specifications of the motor to ensure optimal performance. Sometimes, there’s a trial and error process involved, requiring adjustments to the initial design.
Power motors are essential in various applications, ranging from industrial machinery to household appliances. Understanding their types and characteristics can help optimize their use. The main types include AC motors, DC motors, and stepper motors. Each motor type has unique features that cater to specific needs.
AC motors are known for their durability and efficiency. They are commonly used in HVAC systems and conveyor belts. According to industry reports, AC motors comprise about 40% of all electric motors in use today.
DC motors, on the other hand, offer precise speed control. They are commonly utilized in robotics and electric vehicles. Data shows that DC motors facilitate high torque at low speeds, making them ideal for such applications.
Stepper motors are another critical type. They provide exact positioning by dividing a full rotation into smaller steps. This feature makes them popular in 3D printers and CNC machines. However, they can be less efficient than their counterparts. Users often report overheating issues. Understanding these characteristics aids in selecting the right motor for specific applications. This decision can greatly impact efficiency and performance in operation.
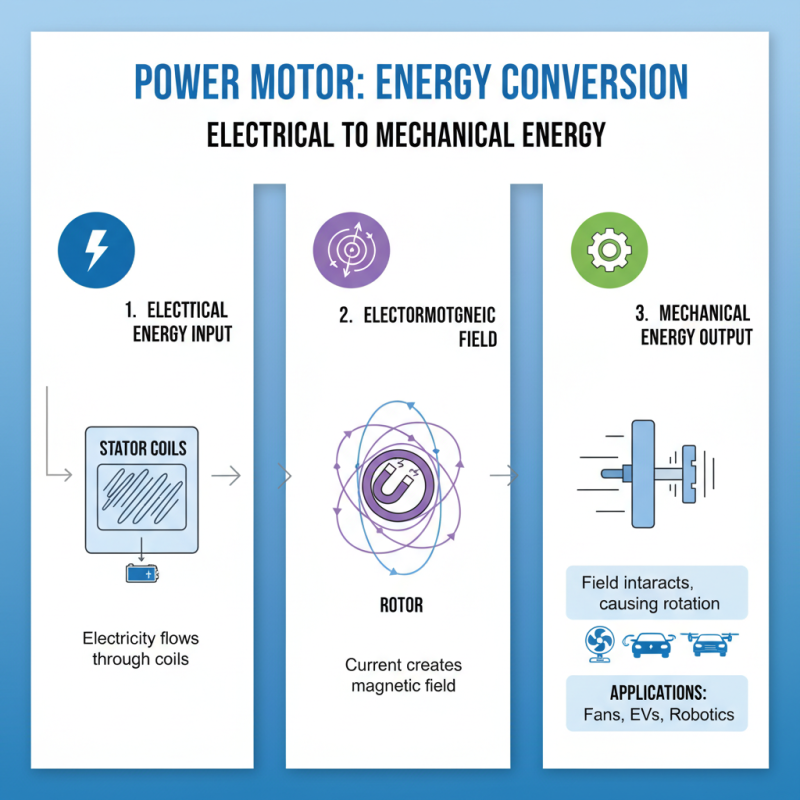
Power motors are fundamental components that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. Understanding their operational principles can help us grasp their significance in various applications. The basic working principle involves electromagnetic fields. When electricity flows through the coils of a motor, it creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field interacts with the motor's rotor, causing it to spin.
Different types of power motors operate on slightly varied principles. For instance, AC motors use alternating current, while DC motors depend on direct current. Each type has distinct characteristics, making them suitable for specific tasks. AC motors are often found in household appliances, while DC motors are common in small devices like toys. However, not every application benefits from these motors equally.
There are challenges with efficiency and performance. Power motors can heat up, affecting their longevity. Additionally, the installation requires careful attention to detail. An improper setup can lead to operational inefficiencies. Power consumption can vary greatly, and this inconsistency raises questions for users. Exploring improvements in their design and function is essential for future advancements. Understanding these operational nuances invites a more critical view of our reliance on power motors.
Power motors play a crucial role across various industries. In manufacturing, they drive conveyor belts, ensuring smooth material transport. These motors can endure harsh conditions. They're built to last, but sometimes they fail under extreme stress. Maintenance is key; neglect can lead to costly downtime.
In agriculture, power motors revolutionize farming. They operate machinery for planting and harvesting. The efficiency gained boosts crop yields. However, reliance on these motors can lead to challenges, like equipment shortages during peak seasons. Farmers must adapt their strategies accordingly.
Power motors are also essential in the renewable energy sector. They help generate electricity from wind and water. This is promising, yet stability issues can arise. Locations with inconsistent wind patterns can reduce effectiveness. Ongoing innovation is necessary to overcome these hurdles. Each application shows the versatility and challenges of power motors in our daily lives.
This chart illustrates the application percentage of power motors across various industries. The automotive sector holds the highest usage at 30%, followed by manufacturing at 25%. Other industries such as aerospace and healthcare show significant but lower usage percentages.
Power motors play a crucial role in various applications, from industrial machinery to home appliances. Their significant advantages include high efficiency and consistent performance. These motors can operate under varying loads, providing the necessary torque without sacrificing speed. This adaptability makes them ideal for diverse settings, whether in manufacturing or transportation.
However, there are limitations to consider. Power motors can be costly to install and maintain. Their complex designs may lead to challenges during repairs. Additionally, power motors often generate heat, which can reduce lifespan and efficiency. Users must ensure proper ventilation. Neglecting this aspect can lead to premature failures. It's crucial for engineers and manufacturers to weigh these pros and cons carefully before integrating power motors into their systems.